The New Modern Mediterranean Diet and The Food Pyramid
Inspired by Italian centenarians and the latest science, the New Modern Mediterranean Diet is a fresh, sustainable approach to healthy eating. This evolution of the classic Mediterranean diet honors cultural diversity and geographical uniqueness, making it globally relevant. It's represented by a new food pyramid that visually guides how often and how much to eat from each food group for optimal well-being.
The New Modern Mediterranean Diet promotes healthy eating in moderation and focuses on a plant-forward diet, enriched by cultural and geographical diversity. This updated version combines the 2020 Updated Mediterranean Diet, the 2014 Italian Nutrient and Energy Guidelines (LARN), and the 2018 Italian Dietary Guidelines, with 13 directives for a healthy diet.
The food pyramid considers unique foods, geography, and cultural contexts, making it adaptable worldwide. The 2023 MedDiet 4.0 framework further extends its global impact, benefiting individuals, communities, and future generations, while preserving the cultural heritage of UNESCO-recognized Mediterranean countries—Cyprus, Croatia, Spain, Greece, Italy, Morocco, and Portugal.
Numerous studies have shown that adhering to the Mediterranean diet reduces the risk of diet-related diseases. Through this website, I aim to introduce this dietary pattern to non-Mediterranean populations as a means of prevention. Using The New Modern Mediterranean Diet Food Pyramid, I develop restaurant-quality international dishes that are easy to prepare at home, using DIY applications or with professional chef assistance.
The Mediterranean diet is both environmentally and economically sustainable, promoting biodiversity and preserving local traditions. The pyramid visually represents consumption frequencies and portions for each food group. At its base are foods to be eaten at every meal, alongside the social, cultural, and environmental elements of the Mediterranean lifestyle. The middle of the pyramid highlights foods for daily consumption, while the top features foods to be consumed weekly.
This pyramid serves as a vital tool for promoting the Mediterranean diet and enhancing adherence to its principles. The DIY Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan Builder™ with chef e-recipes combines science and culinary art to bring The New Modern Mediterranean Diet to your table!
Did you know the Mediterranean DIet has the same core elements as the Healthy U.S. Style Dietary Pattern?
Learn how the MedDiet 4.0 applies to you and to future generations
The Key Components and Frequency of The New Modern Mediterranean Diet Food Pyramid
The Mediterranean Diet Food Pyramid is a comprehensive guide to healthy eating, emphasizing a diverse array of food groups selected for their nutritional value and health benefits. Key components include:
Cereals: Whole grains such as bread, pasta, rice, and couscous are staples, providing essential carbohydrates and fiber. They form the foundation of daily meals, offering sustained energy and supporting digestive health.
Vegetables and Fruits: A cornerstone of the diet, this category encourages the consumption of a variety of colorful, seasonal vegetables and fruits. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, contributing to disease prevention and overall vitality. Daily consumption is recommended, with a focus on variety and abundance.
Olive Oil: As the primary source of dietary fats, olive oil is used generously in cooking, seasoning, and dressing. Rich in monounsaturated fats and polyphenols, it supports heart health and enhances the flavor of dishes. Daily use is a key characteristic of the Mediterranean way of eating.
Wine: When consumed in moderation, particularly during meals, wine is valued for its potential cardiovascular benefits and its role in enhancing the social and cultural aspects of dining. Typically, this means no more than one glass per day for women and up to two for men.
Dairy Products, Nuts, and Seeds: These foods provide essential nutrients like calcium, protein, and healthy fats. Dairy products, particularly yogurt and cheese, are consumed in moderation, while nuts and seeds serve as nutrient-dense options for snacks and meals, promoting bone health and satiety.
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are important sources of plant-based protein, high in fiber and beneficial for heart health. They are recommended several times per week and can be used in various dishes, including soups and salads.
Meats, Seafood, and Eggs: Protein-rich foods are consumed in moderation, with an emphasis on lean proteins like fish and poultry. Seafood, especially oily fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, is recommended at least twice a week, while red meat should be limited to occasional servings.
Sweets and Occasional Indulgences: The diet allows for occasional treats, such as sweets and alcoholic beverages, but moderation is key. These indulgences should be enjoyed sparingly, emphasizing the importance of balance and mindful eating.
Daily Guidelines: the daily recommendations focus on hydration, whole grains, a generous intake of vegetables and fruits, moderate consumption of olive oil, and the inclusion of dairy, nuts, seeds, and legumes. These elements create a balanced, nutrient-rich diet that supports overall health and well-being.
Weekly Guidelines: weekly recommendations encourage variety by incorporating different protein sources, including red meat, white meat, seafood, and eggs. This approach optimizes nutrient intake and promotes dietary diversity, ensuring a well-rounded and satisfying diet.
Occasional Indulgences: Sweets and alcoholic beverages are permitted in moderation, emphasizing mindful consumption. Viewing these as occasional treats rather than dietary staples helps maintain balance and support long-term health.
Customization and Adaptation: The New Modern Mediterranean Diet Pyramid is flexible, allowing individuals to tailor its guidelines to their unique needs, preferences, and dietary requirements. Whether following a vegetarian or omnivorous diet, the pyramid's principles can be adapted to fit various lifestyles and cultural preferences.
The New Modern Mediterranean Diet Pyramid is a valuable tool for promoting health, longevity, and culinary enjoyment. By embracing its principles and making informed food choices, individuals can cultivate a healthy relationship with food and embark on a journey toward better health and well-being.
What Are the Recommended Portions of Food Categories for a Daily Diet?
Tap on the bars below to view the recommended portion sizes for a Mediterranean Diet, based on a daily intake of 2000 kcal for a healthy adult between the ages of 18 and 65. The portions refer to food that has been cooked, with the skin, peel, trimmings, and water removed.
To help you achieve and maintain a healthy BMI, our Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan Builder offers adjustments for daily intakes of 1500 and 2500 kcal. If you are outside the specified age range, pregnant, nursing, or have a medical condition, please consult your doctor before making any dietary changes.
Portion sizes in the chart are indicated in grams for solids and milliliters for liquids. Additionally, please refer to your country’s dietary guidelines, such as the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, for recommended portion sizes.
Food for every day
Include raw and cooked vegetable intake. Fruit juices are not considered a fruit substitute. Cereals and bread intakes should be at least 50% whole grain. In addition, water consumption should be at least 1600 ml a day.
Food for every week
Legumes can be consumed in larger amounts for added protein and fiber, 50 g of dry products can be substituted for fresh ones. Crabs, fish, and shellfish are included in the seafood, whether fresh, frozen, or canned. Rabbit, turkey, and chicken are part of white meat. A medium-sized egg is referred to as an "egg intake." Cow, bull, pork, game, and horse are all considered red meat.
Portion sizes for occasional food
Alcoholic beverages are grouped under the category of occasional food and are for adults only. The maximum indicated portion is 125 ml (1 glass) for wine, 330 ml for beer, 75 ml for vermouths, and 40 ml for sprits.
The Meals for Longevity program is specifically designed based on the principles outlined in The New Modern Mediterranean Diet scientific publication.
Where Are the Sources of The New Modern Mediterranean Diet?
The Meals For Longevity program is guided by scientific research, as referenced in various dietary publications. Explore here below!
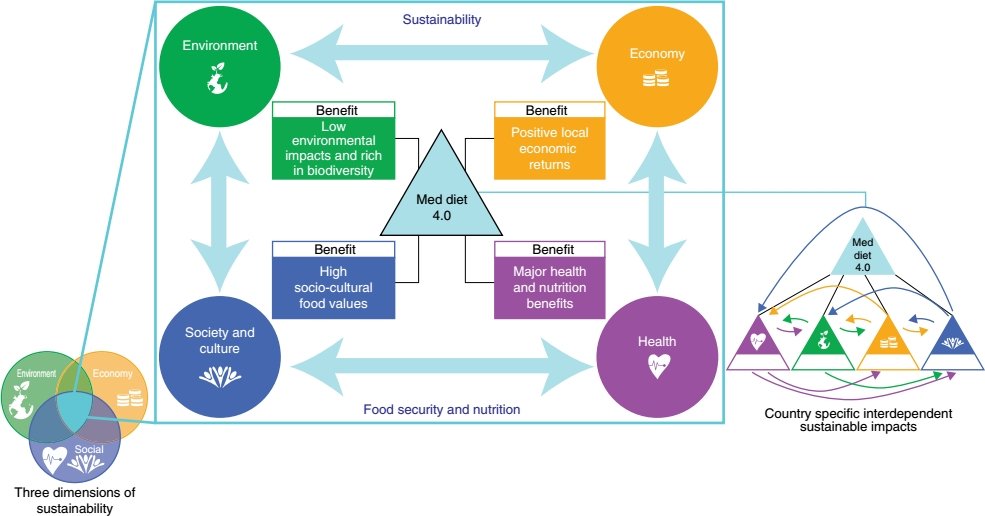
The Med Diet 4.0 framework
The Med Diet 4.0 framework represents a significant evolution in our understanding and promotion of the Mediterranean diet as a sustainable and holistic dietary model. This framework acknowledges the challenges faced by traditional dietary patterns in the Mediterranean region and offers a multidimensional approach to revitalizing the diet for individuals and communities.
Key Points About the Med Diet 4.0 Framework:
Shift Away from Traditional Patterns: Despite being recognized as one of the healthiest diets globally, adherence to the Mediterranean diet has declined in many Mediterranean countries. This shift negatively impacts health, as well as social, cultural, economic, and environmental aspects of life in the region.
Multidimensional Framework: The Med Diet 4.0 framework emphasizes the Mediterranean diet as a sustainable dietary model, focusing on four interdependent benefits:
Nutrition and Health Advantages
Low Environmental Impacts and Biodiversity Richness
Positive Local Economic Returns
High Social and Cultural Food Values
Interconnected Benefits: These four benefits work together synergistically to enhance the holistic well-being of individuals and communities. By promoting these advantages, the Med Diet 4.0 aims to reverse unsustainable dietary trends and foster nutritional well-being and food security in the Mediterranean region.
Educational Focus: The framework stresses the importance of education and communication in promoting the Mediterranean diet. It advocates for personalized educational programs aimed at all age groups, incorporating values such as frugality, simplicity, authenticity, and tradition.
Role in Sustainable Food Systems: The Med Diet 4.0 framework highlights the Mediterranean diet's potential to drive sustainability in food systems. By reconnecting food consumption with production and emphasizing local, seasonal, and traditional food practices, it aims to enhance the environmental, economic, and social sustainability of food systems.
Overall, the Med Diet 4.0 framework offers a comprehensive approach to promoting and revitalizing the Mediterranean diet. It addresses not only health but also broader social, cultural, economic, and environmental dimensions. Through education, communication, and policy interventions, it seeks to ensure the Mediterranean diet remains a relevant and sustainable dietary choice.
